When it comes to global coffee culture, one name consistently stands above the rest: Starbucks. What began as a small coffee bean shop in Seattle in 1971 has grown into the world’s most recognized coffeehouse chain, with over 38,000 stores in 86 countries by the financial year 2025. But Starbucks is far more than a place to enjoy a cappuccino or a caramel macchiato. It is a brand experience—a lifestyle choice—a community in itself.
This case study explores how Starbucks built a billion-dollar brand through smart marketing strategies, emotional customer connections, and continuous innovation. In FY 2025, Starbucks underwent significant changes to stay relevant in a post-pandemic, digitally advanced, and highly competitive world. This study not only showcases their journey but also delivers insights that can help any business leader, student, or marketer understand what makes a brand thrive globally.
A Quick Glance at Starbucks’ Global Reach
As of 2025, Starbucks operates more than:
- 38,000+ stores globally
- 15,000+ outlets in the United States
- 6,000+ stores in Asia Pacific, with India, China, and Japan being major contributors
- Serves over 100 million customers every week
- Employs over 400,000 partners (employees), globally known as “green apron partners”
These figures are more than impressive—they represent how deeply Starbucks has rooted itself into everyday life. In FY 2025, Starbucks reported:
- Revenue of $9.4 billion in Q2 2025
- A 7% year-over-year growth rate
- Over 30 million active users on the Starbucks mobile app in the U.S.
- A digital ordering system that accounts for nearly 30% of all store transactions
These numbers are not just proof of size but demonstrate operational efficiency, customer trust, and digital transformation at scale.
Starbucks’ Unique Positioning: Selling More Than Just Coffee

What makes Starbucks a case study favorite in marketing textbooks and MBA classes around the world? The answer lies in their deep understanding of consumer psychology. Starbucks does not market itself as a place to grab coffee. It promotes itself as:
- A “third place” between work and home
- A lifestyle brand that stands for sustainability, personalization, and quality
- A digital convenience hub with mobile-first features, contactless payments, and app-based rewards
- A brand that supports mental wellness, social causes, and sustainability
Rather than focus on price wars, Starbucks invests in brand loyalty, premium experiences, and consistent quality. It attracts customers who are not just buying a drink—they are buying an identity, a feeling, a ritual.
Changing Customer Expectations Post-Pandemic
Over the last few years, consumer behavior has evolved rapidly. The global pandemic accelerated digital adoption, made people more health-conscious, and shifted preferences toward fast, contactless service. This affected how people consumed coffee and interacted with brands.
In 2025, customers now expect:
- Speed and convenience
- Healthy and customized menu options
- Transparent sourcing and ethical practices
- Strong digital presence and app experience
- Brands that care about employees and communities
Starbucks recognized this shift early and began modifying its operations, marketing efforts, and technology to stay ahead of the curve.
FY 2025: “Back to Starbucks” Strategy Rebuilding the Brand
In 2025, Starbucks launched a major internal and external initiative known as “Back to Starbucks.” Under this mission, the brand decided to return to its core strengths—people, product, place, and purpose.
Here’s what changed in FY 2025:
1. Menu Optimization
Starbucks announced a 30% reduction in menu items to simplify operations, decrease customer wait times, and reduce stress on baristas. This helped improve speed and satisfaction in high-volume stores, especially in the U.S. and China.
2. Human Touch Over Automation
In a world moving fast toward AI and robotics, Starbucks made a bold decision to invest more in human labor than machines. The company focused on:
- Improving employee training
- Giving baristas more autonomy and respect
- Encouraging personalized service (e.g., writing names on cups again)
This move was appreciated by customers who missed the warmth and interaction of a human-led service.
3. Technology Upgrades
Even while returning to traditional values, Starbucks embraced digital innovation. The mobile app introduced features like:
- Real-time store wait time updates
- Queue prioritization
- Personalized menu suggestions based on purchase history
- App-exclusive seasonal beverages
4. Sustainability and Ethics
Starbucks doubled down on its commitment to sustainability in FY 2025. It announced that by 2027, 100% of its cups will be recyclable or compostable. They continued their push for ethically sourced coffee, partnering with over 400,000 farmers worldwide.
The Psychology Behind Starbucks’ Branding

Every decision Starbucks makes is backed by a clear understanding of its audience’s mindset. Their entire brand voice—visuals, music, product naming, interior design, tone in advertising—reflects calmness, comfort, and consistency. This consistency is crucial in today’s market, where customers crave both familiarity and innovation.
For example:
- Starbucks uses earthy green colors to represent calm and nature.
- Stores play lo-fi jazz or soft acoustic music to create a relaxing atmosphere.
- Products are often named with terms that sound aspirational and unique, such as “Honey Almondmilk Flat White” or “Iced Brown Sugar Oatmilk Shaken Espresso.”
Social Media & Influencer Impact
As of 2025:
- Starbucks has over 37 million Instagram followers
- Their #RedCupContest during Christmas receives over 500,000+ entries annually.
- They collaborate with lifestyle influencers and wellness coaches to promote new product launches
- Starbucks India’s local campaigns now feature vernacular content to improve engagement in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities.
Through strong social media storytelling and visually pleasing content, Starbucks creates FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) and community-driven participation, especially among millennials and Gen Z.
StarBucks Awards & Recognition (2024–2025)
In FY 2025, Starbucks continued to shine as one of the most respected, sustainable, and employee-friendly global brands. Its commitment to ethical sourcing, employee empowerment, brand trust, and innovation has earned it numerous recognitions from top international organizations and publications. Here are the notable awards and rankings Starbucks received in 2024–2025:
- Forbes: Top 10 Most Admired Companies
- Sustainability Index: Top Global Coffee Brand for Ethical Sourcing
- Fortune 500: Ranked among the top 100 employers in the world
- Recognized by LinkedIn as a Top Company to Work For in food & beverage.
- Ranked #21 in Interbrand’s Best Global Brands 2025, with a brand value exceeding $20 billion.
- Starbucks retained its position on the CDP Climate A List, recognizing leadership in environmental transparency and performance.
- Starbucks ranked #27 in DiversityInc’s 2025 list, thanks to its diverse leadership pipeline and inclusive workplace practices.
- Starbucks was certified as a Great Place to Work® across North America, Europe, and Asia in 2025.
Starbucks Rewards Program won “Best Loyalty Program” for its digital-first, point-based system with over 35 million active members globally.
Also Read :- Reliance JIO Case Study
Starbucks SWOT Analysis 2025: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats
A SWOT analysis is a valuable tool for understanding a company’s current position in the market. For Starbucks, which has operated for over 50 years and serves millions of customers daily, this analysis helps to uncover why the brand continues to succeed—and where it must adapt. In FY 2025, Starbucks is in a transformation phase, focusing on core customer values, sustainability, and human-led service. Here’s an in-depth SWOT analysis of Starbucks in the current business landscape.
Strengths: The Core Pillars of Starbucks’ Global Success
1. Strong Global Brand Recognition
Starbucks is one of the most recognizable brands in the world. With 38,000+ stores across 86 countries, the company has a massive international presence. The green logo, signature drinks, and friendly ambiance are instantly identifiable, even in markets where coffee isn’t the dominant beverage.
2. Premium Customer Experience
Starbucks doesn’t just sell coffee; it sells an experience. The focus on clean interiors, calming music, and cozy seating turns each outlet into a “third place” between home and work. In FY 2025, the brand doubled down on this, bringing back personal touches like writing names on cups and self-service condiment bars.
3. Technological Leadership
With over 30 million app users in the U.S. and mobile orders accounting for nearly 30% of all transactions, Starbucks leads in digital transformation. Features like queue optimization, loyalty points, and app-exclusive offers have enhanced customer convenience.
4. Employee-Centric Culture
Starbucks refers to its staff as “partners,” offering them stock options, training, and career growth. In 2025, the brand took a human-first approach, reducing dependency on automation and investing more in baristas to improve service quality.
5. Ethical and Sustainable Practices
Starbucks sources 99% of its coffee through ethical practices via Coffee and Farmer Equity (C.A.F.E.) programs. Its sustainability goals—like recyclable packaging by 2027—attract environmentally conscious consumers.
Weaknesses: Areas That May Limit Growth
1. Premium Pricing
Starbucks positions itself as a luxury coffee brand. While this has worked in urban and developed markets, it can alienate price-sensitive customers in Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities in India or emerging economies in Africa and Southeast Asia.
2. Menu Complexity
Until FY 2024, the large and complicated menu led to long waiting times, especially during rush hours. In FY 2025, Starbucks responded by reducing its menu by 30%, but the complexity remains in some regions.
3. Overdependence on the U.S. Market
Although Starbucks has global reach, a significant portion of its revenue still comes from the U.S. This makes the company vulnerable to market saturation, changing domestic consumer habits, and economic shifts.
4. Operational Challenges in New Markets
Entering new countries often means facing local competition, high setup costs, and cultural adaptation. In some countries, Starbucks has closed stores due to poor performance and high real estate expenses.
Opportunities: Future Areas for Expansion and Innovation
1. Growing Coffee Demand in Emerging Markets
Countries like India, Indonesia, and Vietnam are witnessing a coffee culture boom. Starbucks can grow rapidly in these regions by introducing localized products, affordable menus, and region-specific branding.
2. Health-Conscious and Plant-Based Trends
With rising demand for plant-based milk alternatives, low-sugar drinks, and protein-rich options, Starbucks can expand its health-focused product lines. In FY 2025, offerings like almond milk lattes and oat-based beverages saw a 17% rise in sales.
3. Expansion in Drive-Thru and Delivery
Post-pandemic lifestyles have created lasting demand for convenience. Starbucks is expanding drive-thru-only outlets and partnering with food delivery apps like Swiggy, Zomato, and Uber Eats to tap into the quick-service space.
4. Corporate and Co-Working Tie-Ups
In 2025, hybrid work is the norm. Starbucks can collaborate with corporate hubs, co-working spaces, and colleges to create exclusive in-store experiences or pop-ups, driving weekday footfall.
5. Product Innovation and Seasonal Promotions
Limited edition beverages like the Pumpkin Spice Latte or Holi-themed drinks in India boost customer excitement. Creating region-specific seasonal drinks can keep customers engaged all year.
Threats: Market Forces That Challenge Growth
1. Increasing Competition
From Dunkin’ Donuts, Tim Hortons, and Costa Coffee, to local startups and specialty cafes, competition is fierce. In India alone, Chaayos and Blue Tokai are gaining market share by offering unique flavors at better prices.
2. Rising Raw Materials and Labor Costs
Global inflation in FY 2025 has increased the cost of coffee beans, dairy, sugar, and labor. Starbucks faces pricing pressure, but it can’t always pass these costs on to consumers without risking customer loss.
3. Economic Recession and Inflation
With inflation hitting several global markets and consumer budgets tightening, people are cutting back on non-essential purchases, like premium coffee. This affects Starbucks’ store traffic in low-income and developing regions.
4. Geopolitical Risks and Regulatory Issues
Tariffs, import restrictions, and labor laws can affect Starbucks’ supply chain and profitability. For instance, political tensions in China affected brand perception, leading to a dip in sales growth in 2023–2024.
5. Changing Customer Behavior
In 2025, Gen Z customers demand more ethical, affordable, and socially responsible choices. If Starbucks fails to align quickly with its evolving expectations, it risks losing relevance.
Conclusion of SWOT
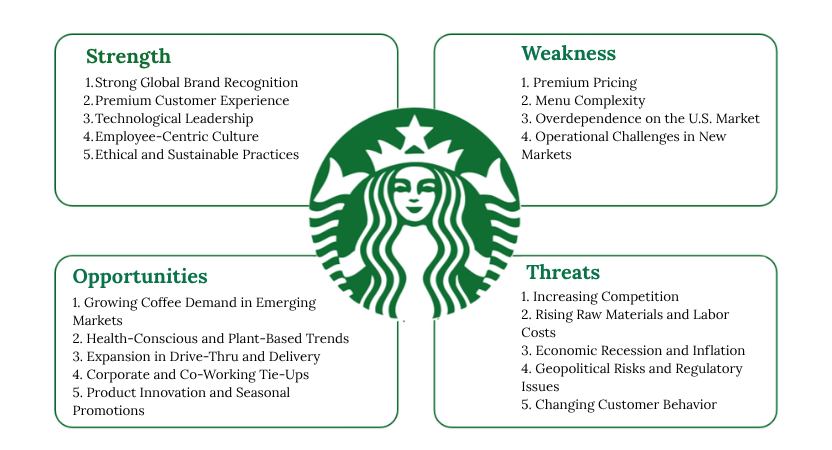
Starbucks’ Strengths lie in its brand loyalty, ethical values, and digital innovation. While Weaknesses such as pricing and operational complexity persist, the company has shown a willingness to evolve. The Opportunities in emerging markets and health-based products can fuel future growth, but Threats like competition and inflation need a proactive strategy and brand resilience.
The key learning here? Even the world’s biggest brands must constantly rethink, refocus, and reinvent—just like Starbucks is doing in 2025.
Starbucks proves that great branding is not about having the biggest budget—it’s about having clear values, strong execution, and constant evolution. In FY 2025, the brand didn’t just focus on selling more coffee—it focused on rebuilding relationships, both with customers and its team.
Learnings
For students, marketers, entrepreneurs, and small business owners, the biggest lesson is this: Great marketing is not about manipulation—it’s about meaning. If your business can touch people’s lives and add real value, success will follow, just like it has for Starbucks.
Also Read :- Zomato Case Study

